As I started the System Architect journey, I found some topics to be more vital in succeeding the exam. Even though there may be a lot on the certification on Trailmix already, but here are some that I would particularly like to mention:
Components of Governance Framework:
Three elements of a responsive and adaptable framework for governance
A few stakeholders from different functional groups work together to ensure that changes support business goals and follow IT best practices and processes. Teams that can be part of COE:
2- Release Management:
Set up a release schedule and defining criteria for major versus minor releases.
Releases typically fall into one of the following categories: Daily, Minor, Major
Daily: Bug fixes and simple changes that do not require formal release management, including reports, dashboards, list views, email templates, and user administration.
Minor: Changes with limited impact, such as a new workflow rule or trigger impacting a single business process. These releases typically require testing, but limited training and change management, and are delivered within a few weeks.
Major: Changes with significant impact, including configuration and code changes with one or more dependencies
Its important to have design standards for the following keys areas: Coding, Testing, Integration, Handling Large data Volumes and Documentation.
Some examples of design standards include:
- Standard naming conventions
- Consistently using the Description field
- Bulkified code
- Standard methods for deprecating classes and fields
- Consistent data architecture across all projects
Metadata API:
Here are some key points. You can find all details here
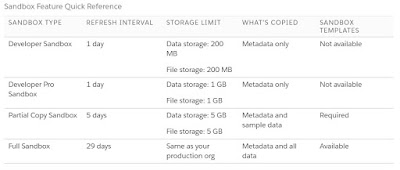
Sandbox License and Storage by Type:
- Use Metadata API to retrieve, deploy, create, update or delete customization information, such as custom object definitions and page layouts, for your organization.
- List of Components which are not supported in Metadata API. Details here
- You can deploy or retrieve up to 10,000 files at once and the maximum size of the deployed or retrieved .zip file is 39 MB.
- The size and complexity of the metadata components affect the deployment time.
Sandbox License and Storage by Type:
You can create different sandbox environments for your org, depending on your needs for storage, copy configuration, and frequency of refresh. Details here
Application Lifecycle Management:
Salesforce provides various development tools and processes to meet the needs of customers. This module introduces the application lifecycle management (ALM) process and the three development models. Details here
Salesforce provides various development tools and processes to meet the needs of customers. This module introduces the application lifecycle management (ALM) process and the three development models. Details here
- Change set development
- Org development
- Package development
Effective Change Management
Change Set Development Model
Force.com IDE Basic
Governance Basics
I hope this information is useful for getting you through the exam. Feel free to comment below if you require further details. Good luck on the exam!
Change Set Development Model
Force.com IDE Basic
Governance Basics
I hope this information is useful for getting you through the exam. Feel free to comment below if you require further details. Good luck on the exam!